In the most recent test, the weapons were tested in Alaska at temperatures of -37 degrees Celcius, as reported by the Defense Post.
Following the SIG Sauer’s selection in the programme, the next testing stage began for XM7 and XM250. Both guns are planned to replace M16 and M249 squad weapons in the future. Within a 10-year span, 18000+ NGSW weapons are planned to be procured at a cost of $331 million.
XM7 and XM250 use the new 6.8x51 mm round, based on .277 Fury. 6.8x51 mm has a higher stopping power than 5.56x45 mm NATO and reportedly better performance at longer ranges than the widely used 7.62x51 mm NATO. XM7 feeds from 20-round magazines, while XM250 is belt-fed.
The idea of using the 6.8x51 mm came with the request for ammunition that can penetrate military-grade body armour at longer ranges and outmatch the 7.62x51 mm in terms of ballistic performance.
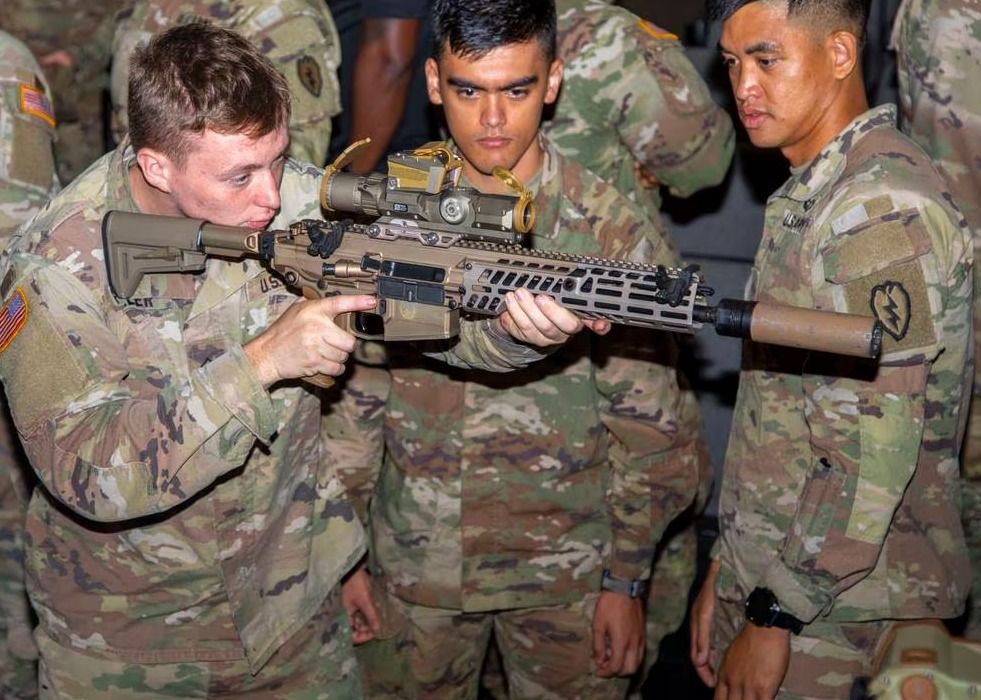

Both weapons use the XM157 fire control optic, fitted with a ballistic computer that compensates for bullet drop and wind for better precision at longer ranges.
When both weapons are inspected, they can be observed to be designed to defeat a peer armed force, sharing the current capabilities in mind.
However, this way of development can be viewed as over-costly, with an average price tag of about $18300 per unit. Even though this is the initial cost, using expensive components like the fire control optic and ammunition can only allow the cost to be pulled down to a certain point.